Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can have serious consequences if left undiagnosed. In this article, we will guide you through the step-by-step process of how sleep apnea is diagnosed.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep apnea diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and sleep tests.
- Polysomnography (PSG) and Home Sleep Testing (HST) are two common sleep tests used to diagnose sleep apnea.
- Diagnosis of sleep apnea can also involve evaluating symptoms, medical history, and physical examination.
Initial Evaluation
The diagnosis of sleep apnea typically begins with an initial evaluation by a healthcare professional. This evaluation involves:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | A thorough physical examination to check for signs of sleep apnea, such as high blood pressure, obesity, and a large neck circumference. |
| Medical History | A review of the patient's medical history to identify potential risk factors and underlying conditions that may contribute to sleep apnea. |
| Symptom Evaluation | An evaluation of the patient's symptoms, such as snoring, daytime sleepiness, and fatigue. |
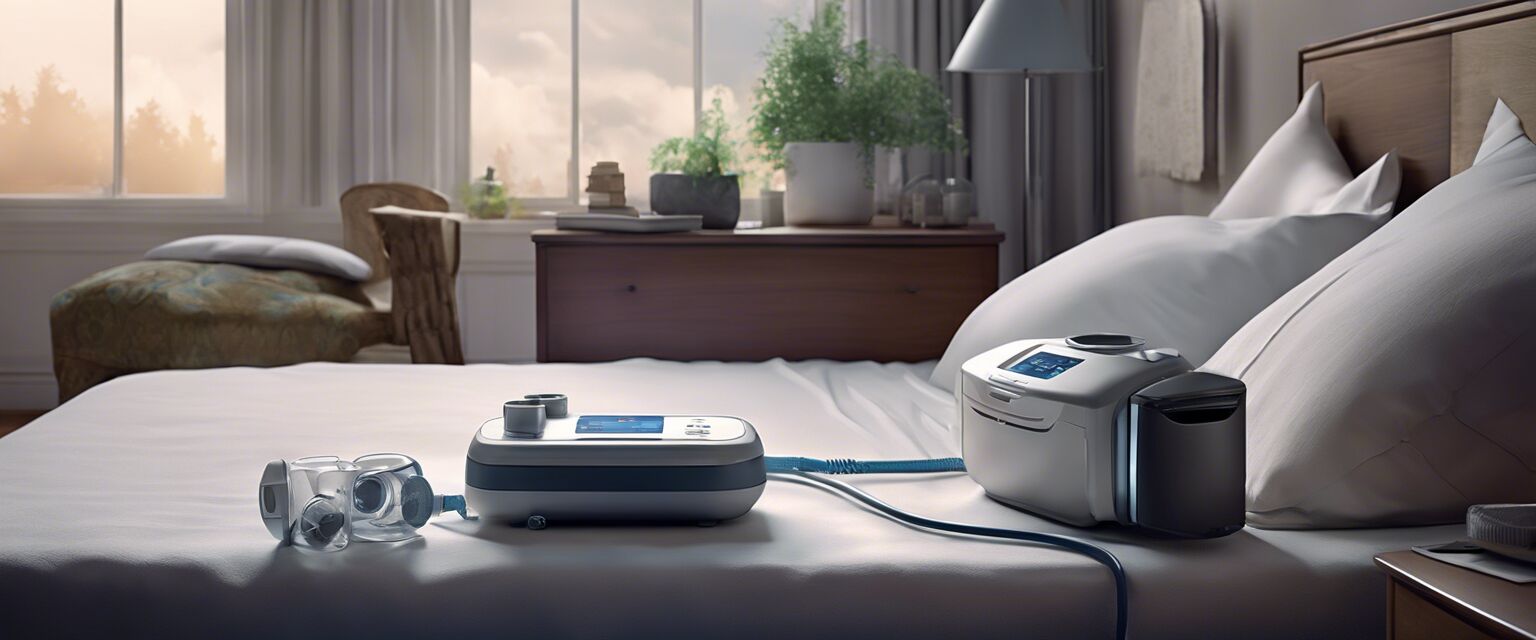
Sleep Tests
After the initial evaluation, the healthcare professional may recommend one or more sleep tests to confirm the diagnosis of sleep apnea.
| Sleep Test | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polysomnography (PSG) | A comprehensive sleep test that records various physiological activities during sleep, such as brain waves, muscle activity, and heart rate. | Provides detailed information about sleep patterns and can diagnose other sleep disorders. | Requires an overnight stay in a sleep laboratory, can be expensive. |
| Home Sleep Testing (HST) | A portable sleep test that records sleep patterns and breathing during sleep in the comfort of the patient's own home. | Less expensive, more convenient, and can be used for ongoing monitoring. | May not provide as detailed information as PSG, may not diagnose other sleep disorders. |

Diagnosis and Treatment
After the sleep test results are evaluated, the healthcare professional will diagnose sleep apnea based on the severity of the symptoms and the results of the sleep test.
Treatment for sleep apnea typically involves lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and exercise, as well as the use of CPAP machines or other sleep therapy devices.
Beginners Section
- If you suspect you or a loved one has sleep apnea, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Learn more about sleep apnea and its treatment options by exploring our resources on CPAP masks and accessories and humidifiers for sleep therapy.
Advantages of Early Diagnosis
- Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious health consequences, such as heart disease and stroke.
- Improved sleep quality and reduced daytime sleepiness.
Consequences of Delayed Diagnosis
- Increased risk of serious health consequences, such as heart disease and stroke.
- Ongoing sleep disturbances and daytime sleepiness.